Suggest Type | Description |
|---|---|
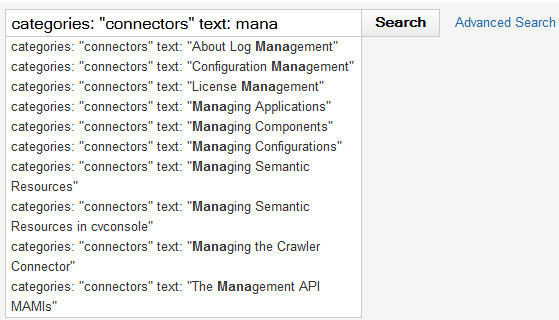
Suggest from the index | These take the result of an index query and build a suggest dictionary from a part of each hit. You can use this to either build a suggest dictionary based on the whole index, by using "#all" as the query, or to restrict to a subset of the index. • Index field suggest – Takes the value of an index field. You can enable security for this type of suggest (expand the Build options node). It uses both documents and user security tokens to restrict suggestions. To build suggests on alphanumeric index fields, see also Performance Considerations and Options for Search Suggest. • Category title suggest – Takes all category titles from a subpath of one category index field. • Category path suggest – Takes all category paths from a subpath of one category index field. • CSV index field suggest – Takes one value from a multiencoded CSV field, also known as the "metas" field in the default configuration. • Related terms suggest – Takes the value of the keyword field. |
Suggest from query reporting logs | The option Query reporting suggest automatically builds a suggest dictionary from all stored query logs. These query logs also serve for search reporting (see Analyzing User Queries with Reporters). |
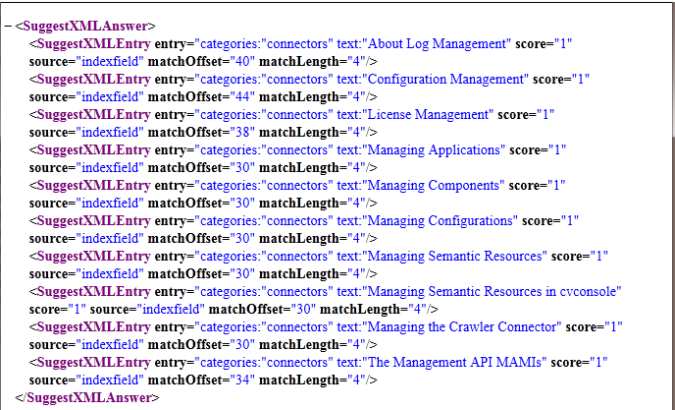
Suggest from a custom XML dictionary | If you want to suggest dictionary from an external data source, use the Static XML suggest option: • Create your own XML dictionary (see XML dictionary structure below). • Place the XML file on the server hosting the main gateway. In the Administration Console, add a Static XML suggest and give the path to the XML file, prepending it with "file://" (for example file:///data/mydir/mydictionary.xml). The root node of the XML file is SuggestDictionary, it contains: • a set of SuggestDictEntry • maxEntries • subExpr • subString Each entry of the dictionary is defined by a SuggestDictEntry node, which contains the attributes: • entry – the expression to match • score – the score • display – what must be displayed A suggest dictionary entry can contain alternative expressions. For example, if you want to add synonyms ("resto" for "restaurants"), you can add a SuggestDictEntryAlternativeForm node inside SuggestDictEntry. This specific node contains two attributes: • form - the alternative expression to add • score - the score of the alternative form, if not set we use the score of SuggestDictEntry Example: Here the Suggest query "a" returns 3 results: "aircraft", "airlines", "air". <sugg:SuggestDictionary xmlns="exa:com.exalead.mot.suggest.v10" maxEntries="3" subExpr="false" subString="false" > <sugg:SuggestDictEntry entry="airport" score="1" display="Airport" /> <sugg:SuggestDictEntry entry="air" score="2" display="Category:Air" /> <SuggestDictEntry entry="airlines" score="3" display="Airlines"/> <sugg:SuggestDictEntry entry="aircraft" score="4"/> <sugg:SuggestDictEntry entry="airelles" score="1" /> <sugg:SuggestDictEntry entry="airpower" score="1" /> <sugg:SuggestDictEntry entry="trucpower" score="1" /> <sugg:SuggestDictEntry entry="restaurant" score="10"> <sugg:SuggestDictEntryAlternativeForm form="resto" score="2" /> </sugg:SuggestDictEntry> </sugg:SuggestDictionary> Example with extra information: A Suggest dictionary entry can also contain a set of extra information (a set of URL for example), stored in SuggestDictEntryExtraInfo. Extra information are strings associated to each entry. They are returned by the suggest API when doing a query. You can also store the information in SuggestDictEntryKeyValue if you want to store a set of keys/values. In this example, the entries "airport", "air", "aircraft" and "airelles" have extra information. <sugg:SuggestDictionary xmlns="exa:com.exalead.mot.suggest.v10" maxEntries="3" subExpr="false" subString="false" > <sugg:SuggestDictEntry entry="airport" score="1"> <sugg:SuggestDictEntryExtraInfo info="http://www.c.com"/> <sugg:SuggestDictEntryExtraInfo info="http://www.d.com"/> </sugg:SuggestDictEntry> <sugg:SuggestDictEntry entry="air" score="2"/> <sugg:SuggestDictEntry entry="airlines" score="3" /> <sugg:SuggestDictEntry entry="aircraft" score="4"> <sugg:SuggestDictEntryKeyValue key="url.first" value="http://www.a.com"/> <sugg:SuggestDictEntryKeyValue key="url.second" value="http://www.b.com"/> </SuggestDictEntry> <sugg:SuggestDictEntry entry="airelles" score="1" > <sugg:SuggestDictEntryExtraInfo info="http://www.e.com"/> </sugg:SuggestDictEntry> <sugg:SuggestDictEntry entry="airpower" score="1" /> <sugg:SuggestDictEntry entry="trucpower" score="1" /> </sugg:SuggestDictionary> |
Suggest from a custom precompiled resource | A static resource suggest takes an already-compiled suggest dictionary as a parameter. This dictionary is loaded by the search server suggest command to answer queries. All the suggest types available in the Administration Console help retrieving the entries that must be compiled to produce this suggest resource. This suggest dictionary cannot be scheduled or built. |
Option | Description |
|---|---|
Distance | Allows approximate matching. The higher the distance the more approximate the match. • 0: exact match. • 1: distance tolerance of 1 between the result and the query • 2: distance tolerance of 2 between the result and the query For more information about approximate matching, see Approximation. |
Autocomplete | Appends suggest results to the last query word entered in the search field to autocomplete it. It only applies to suggests built with the Subexpr matching or Substring matching build options. |
Recursive | Discards the leftmost word of the query progressively. It sends each new subquery to the suggests until you reach the max number of suggestions, or until there is no more word to use. For example, for a query "A B C", the suggest is called 3 times, with "A B C", "B C", and "C". |
Build option | Description |
|---|---|
Subexpr and Substring matching | Normally, suggest matching is prefix-based: "first" returns entries "first test" and "first image". Sometimes, you want to be able to do a wider matching, not always prefix-based. • Subexpr matching allows you to find matches on every start of word. For example, "first test" returns both for "fir" and for "tes". • Substring matching allows you to find matches on every letter. For example, "first test" returns for "fir", for "rs", for "es", ... |
Sentence split and Ngram split | For performance reasons, use these options to avoid long entries. By "long", we mean entries longer than 100 characters (100 bytes). Sentence and ngram split options allow you to break up a suggest entry into several entries, and to perform matches independently on the chunks. • For sentence split, if the entry is multisentence, an entry is created for each sentence. • For ngram split, a sliding window of ngrams of a given size is created and an entry created for each step of the window. For example, "a b c d e f" with a split on 4-grams gives entries "a b c d", "b c d e", "c d e f". Note: 0 means no splitting. |
Compute permutations | Computes all permutations for an entry and adds them as separate entries. For example, if you start entering "Angeles", Exalead CloudView automatically suggests "Los Angeles". Note: Entries longer than 8 words are not permuted for performance reasons. This action is performed after the sentence split if the Sentence split option is selected. To apply permutation to Static XML suggest and Static resource suggest types, you need to add permutation="true" to the SuggestDictionary tag in your XML file or suggest resource in the Business Console. |
Max. entry length | The maximum number of characters in a suggest entry. This is a security measure to prevent overly long entries. They are automatically truncated after the specified length. 0 means no limit. |
Max. suggestions | The maximum number of suggestions that can be shown to the user for a given input string. You cannot change this dynamically. |
Tokenization config | Specifies the Tokenization configuration to use. |
Sanitize entry | This option strips the entry of punctuation, and encloses any UQL operators in quotes. It is useful when you want to suggest among a list of product references containing "-" (hyphens) or other delimiters, and you do not want any tokenization on these characters. |
Build after import | Triggers a build automatically after the index refreshes. |
Enable security | Makes use of documents and users’ security tokens to restrict suggestions. |
Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
q | string | The input query |
distance | integer (0, 1, 2) | The suggest dictionaries supports fuzzy matching at runtime. This specifies the maximum Levenshtein distance between the input string and the suggestion. 0 means exact match |
minLenForDist1 | integer | Only searches for distance 1 fuzzy matches if the original word in the query is at least N characters long. This avoids too much approximation on very short words. The suggested value is 3. |
minLenForDist2 | integer | Only searches for distance 2 fuzzy matches if the original word in the query is at least N characters long. This avoids too much > approximation on very short words. The suggested value is 6. |
logic | string | Specify a Search Logic name. |
exhaustive | true/false Boolean | Displays exhaustive results. |
recurse | true/false Boolean | Suggests new matches on query words recursively. |
autocomplete | true/false Boolean | Suggests matches for the last word only. |
output | string (xml or json) | Output format: • xml – returns a complete output, with text suggestions, score, distance. • json – returns text suggestions only. Other search output format such as csv, flea, and atom, are not supported. Note: The Accept HTTP header is also taken into account if output is not specified. |
callback | string | When using JSON output, the name of a Javascript function to call. The returned Javascript fragment is "callback && callback(json_object)". |
Option | Description |
|---|---|
Match whole query | Sends the whole query to the default suggest if the cursor is outside a prefix handler. For example, if the query is: author: "George Lucas" Star Wars If the cursor is after the last quote, you are outside the author: prefix handler scope, and: • If the option is selected, the suggest is made on the whole query, author: "George Lucas" Star Wars • If cleared, the suggest is applied to Star Wars only. author: "George Lucas" is not considered. |
Use default suggest for non configured prefix | Sends the query to the default suggest if the cursor is within an undefined prefix handler. If cleared, undefined prefix handlers are ignored and there is no suggestions. |
Add quotes to suggestions | Adds quotes where required so that the whole suggestion is included in the prefix handler. |
Add prefix handler to suggestions | Adds prefix handlers automatically when you enter a query |
Check with search logics | Selecting specific search logics allows prefix handler suggestion and configuration check while configuring prefix handler/suggest pairs below. |
Max. suggestions | Allows you to define a maximum number of suggestions to be displayed (default is 0, meaning no limit). Note: You can also define a maximum number of suggestions to be displayed for each prefix handler. See below. |
Boost variety | Allows to retrieve the best matches for each suggest according to the maximum number of suggestions defined previously. Note: This mode does not return the best global results but the best results for each suggest. Example: a suggest dispatcher is configured to display 10 suggestions maximum, for 3 suggest dictionaries. Without Boost variety, you get: • Suggest 1: 3 results • Suggest 2: 10 results • Suggest 3: 8 results With Boost variety, you get: • Suggest 1: 3 results • Suggest 2: 4 results • Suggest 3: 3 results |
Prefix handler | Suggest | Maps a prefix handler to a suggest dictionary. You can map as many pairs as required. Select Default to specify the suggest dictionary to use by default for a specific prefix handler. Note: You must specify at least one default suggest, using the following options: • Match whole query • Use default suggest for non configured prefix • Add prefix handler to suggestion If required, define a maximum number of suggestions to be displayed for each prefix handler in the Max. suggestions field. |